题目
Description
Bean-eating is an interesting game, everyone owns an M*N matrix, which is filled with different qualities beans. Meantime, there is only one bean in any 1*1 grid. Now you want to eat the beans and collect the qualities, but everyone must obey by the following rules: if you eat the bean at the coordinate(x, y), you can’t eat the beans anyway at the coordinates listed (if exiting): (x, y-1), (x, y+1), and the both rows whose abscissas are x-1 and x+1.
Now, how much qualities can you eat and then get
Input
There are a few cases. In each case, there are two integer M (row number) and N (column number). The next M lines each contain N integers, representing the qualities of the beans. We can make sure that the quality of bean isn't beyond 1000, and 1<=M*N<=200000.
Output
For each case, you just output the MAX qualities you can eat and then get.
Sample Input
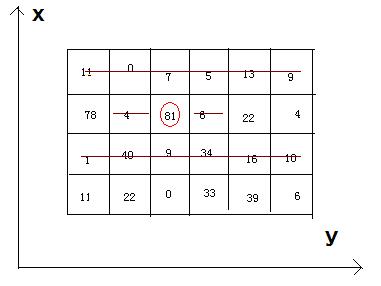
4 6
11 0 7 5 13 9
78 4 81 6 22 4
1 40 9 34 16 10
11 22 0 33 39 6Sample Output
242
翻译
背景
吃豆子是一个有趣的游戏,每个人都拥有一个
M*N矩阵,这里充满了不同质量豆子
每个网格中只有一个豆子
任务是收集最多的豆子
但必须遵守以下规则:
如果吃了坐标是(x,y)的豆子,则不能吃以下坐标的豆子(如果存在):
(x,y-1),(x,y + 1),横坐标为x - 1,x + 1的两行输入
多组数据输入
每组数据先输入格数M、N分别代表M行N列
接下来M行每行有N个数,代表这个格子豆子的质量
豆子的质量小于1000
1<=N*M<=200000
题解
对于每一行,需要找出该行的最大不连续子序列
记录下每行这个最大的值
再对于整个图,在每行的最大值中,找出最大不连续子序列
此时求得的数,就是我们需要的答案
代码
/* By:OhYee Github:OhYee HomePage:http://www.oyohyee.com Email:oyohyee@oyohyee.com かしこいかわいい? エリーチカ! 要写出来Хорошо的代码哦~ */ #include <cstdio> #include <algorithm> #include <cstring> #include <cmath> #include <string> #include <iostream> #include <vector> #include <list> #include <queue> #include <stack> #include <map> #include <set> using namespace std; const int maxn = 200005; int numt[maxn]; int num[maxn]; int dp[maxn]; int N,M; bool Do() { if(scanf("%d%d",&N,&M) == EOF) return false; memset(dp,0,sizeof(dp)); for(int i = 1;i <= N;i++) { for(int j = 1;j <= M;j++) { int temp; scanf("%d",&temp); if(j <= 2) { if(j == 1) numt[j] = temp; else numt[j] = max(numt[1],temp); } else { numt[j] = max(numt[j - 1],numt[j - 2] + temp); } } num[i] = numt[M]; } dp[1] = num[1]; dp[2] = max(num[1],num[2]); for(int i = 3;i <= N;i++) { dp[i] = max(dp[i - 1],dp[i - 2] + num[i]); } printf("%d\n",dp[N]); return true; } int main() { while(Do()); return 0; }



 中文博客导航
中文博客导航
 萌ICP备20213456号
萌ICP备20213456号

