题目
Description
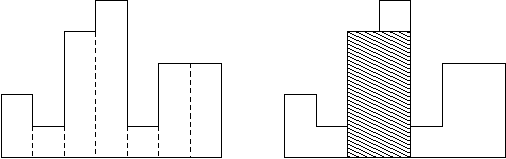
A histogram is a polygon composed of a sequence of rectangles aligned at a common base line. The rectangles have equal widths but may have different heights. For example, the figure on the left shows the histogram that consists of rectangles with the heights 2, 1, 4, 5, 1, 3, 3, measured in units where 1 is the width of the rectangles:
Usually, histograms are used to represent discrete distributions, e.g., the frequencies of characters in texts. Note that the order of the rectangles, i.e., their heights, is important. Calculate the area of the largest rectangle in a histogram that is aligned at the common base line, too. The figure on the right shows the largest aligned rectangle for the depicted histogram.Input
The input contains several test cases. Each test case describes a histogram and starts with an integer n, denoting the number of rectangles it is composed of. You may assume that 1 <= n <= 100000. Then follow n integers h1, ..., hn, where 0 <= hi <= 1000000000. These numbers denote the heights of the rectangles of the histogram in left-to-right order. The width of each rectangle is 1. A zero follows the input for the last test case.
Output
For each test case output on a single line the area of the largest rectangle in the specified histogram. Remember that this rectangle must be aligned at the common base line.
Sample Input
7 2 1 4 5 1 3 3
4 1000 1000 1000 1000
0Sample Output
8
4000
翻译
背景描述
直方图是在同一条底线上由多个正方形构成的图形.每个正方形宽度相同,但是高度可能不同.
举例来说,如下图,用宽度为单位1,左侧的直方图有着高度分别为2,1,4,5,1,3,3
通常,直方图被用作描述离散分布关系通常,使用直方图来表示离散分布
例如:数据的频率
注意数据的顺序
另外:他们的高度也是很重要的
计算最大矩形的面积直方图中常见的基线对齐.右边的图显示了直方图的最大矩形.输入
输入包括多组数据
每组数据描述了一个直方图。
数据以n开始,表示了长方形的数目(1<=n<=100)
而后包括n个整数h1,h2……hn(0<=hn<=1000000000)
这些数据从左到右描述了长方形的高度
长方形的宽度为1
在所有数据的最后是一个0输出
对于每组数据,在一行内输入一个整数,表示直方图最大的长方形面积
长方形必须在底部的基线对齐
题解
如果暴力枚举的话,需要枚举左边界 l 和右边界 r 同时要计算范围内高度的最小值
时间复杂度是 O(n2)
由于是 dp 专题,尝试使用 dp 的思路求解
首先要找到状态关系
对于 i 我们可以根据所有小于 i 已求得的数据来计算出 i 的结果
如果自己数的话,可以将所有非递增的小矩形看成一个整体
每组矩形里,最小的是小组内最后一个矩形
维护 Begin、Min 两个数组,分别记录 i 对应的小组第一个元素的下标和小组最小的元素的值
对于新读入的 h
只需要判断 i ( h 的下标)到每个 <=i 的 Begin 组成的矩形即可
然而,仔细分析,发现这种方法还是超时,在最坏情况下其实是与暴力解法是一样的
换一种思路
如果枚举高度
计算每种高度所能达到的最大值,再找它的最大值
对于 i 在没有遇到比它高的数的前提下,尽可能向左向右拓展
所能达到范围,就是这个高度所能取得的最大宽度
而高度就是其本身高度
对于两个同样高度的矩形
如果他们在同一区域,能拓展到对方,则相当于重复计算了一次
如果不在同一区域,则相当于计算了两组数据
使用这种算法,在找好 l 和 r 数组后,只需要 O(n) 的时间
而如果直接生成 l 和 r 数组,时间复杂度又成了 O(n2)
因此可以采用动态规划的思路
类似上面只判断每一组端点的方法
先向左、向右刷一遍数组,对每个 i 跳着找到端点
如果有一次遇到最坏情况,则必然有一个是最好情况与其对应
因此尽管最坏是O(n2)但是实际运行会好很多
代码
/* By:OhYee Github:OhYee Blog:http://www.oyohyee.com/ Email:oyohyee@oyohyee.com かしこいかわいい? エリーチカ! 要写出来Хорошо的代码哦~ */ #include <cstdio> #include <algorithm> #include <cstring> #include <cmath> #include <string> #include <iostream> #include <vector> #include <list> #include <queue> #include <stack> #include <map> #include <set> #include <functional> using namespace std; typedef long long LL; const int INF = 0x7FFFFFFF; const int maxn = 100005; int l[maxn]; int r[maxn]; LL h[maxn]; bool Do() { int n; scanf("%d",&n); if(n == 0) return false; for(int i = 1;i <= n;i++) scanf("%lld",&h[i]); h[0] = h[n + 1] = 0; for(int i = 1;i <= n;i++) { int t = i; while(t > 1 && h[i] <= h[t - 1]) t = l[t - 1]; l[i] = t; } for(int i = n;i >= 1;i--) { int t = i; while(t < n && h[i] <= h[t + 1]) t = r[t + 1]; r[i] = t; } LL Max = 0; for(int i = 1;i <= n;i++) { Max = max(Max,(r[i] - l[i] + 1)*h[i]); } printf("%lld\n",Max); return true; } int main() { while(Do()); return 0; }



 中文博客导航
中文博客导航
 萌ICP备20213456号
萌ICP备20213456号

